Breast
Contents of this page
- Ultrasound images of lactating breast
- Carcinoma of breast
- Carcinoma of breast: case-2
- Breast cancer- case-3
- Carcinoma breast -case-4
- Oil cyst of breast
- Galactocele of breast
- Galactocele with fluid level
- Breast Abscess
- Fibroadenoma of breast
- Giant fibroadenoma or Juvenile fibroadenoma
- Phyllodes tumor of the breast
- Fibroadenosis of breast
- Ultrasound imaging of Breast implant
- Breast seroma following lumpectomy for breast carcinoma
- carcinoma breast with liver metastasis
- simple breast cysts
- carcinoma-breast-with-axillary-node
- mastitis-left-breast
- multiple-juvenile-fibroadenomas-breast
- inflammatory-carcinoma-breast
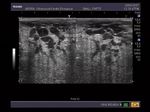
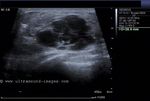
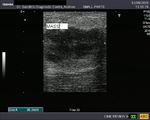
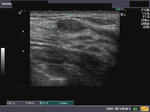
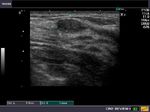
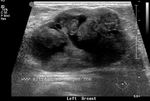
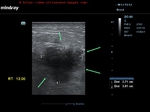
Ultrasound images of lactating breast
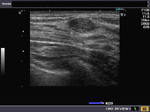
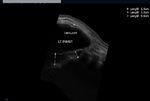
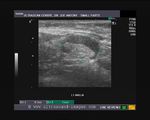
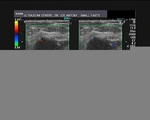
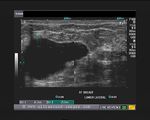
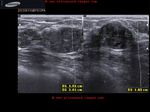
This ultrasound image shows prominent and dilated mammary ducts in the lactating breast. The ducts are seen as tubular hypoechoic structures, which widen as they approach the nipple. Sometimes, it may be possible to see fat drops within the milk secretions in the ducts. These appear as mildly echogenic debris within the ducts. Image taken using a Toshiba Nemio 30 ultrasound scanner, courtesy of Dr. Vikas Arora, India.
Reference: 1) (free article and images--> rated excellent).
Download this excellent e-book and read in Amazon kindle app on your mobile, tab or Kindle reader:
Atlas of breast ultrasound.
This atlas of sonography of almost every pathology of the breast is presented in Atlas format using the best high resolution ultrasound images.Presented and authored by Dr. Joe Antony, MD
Click here: https://www.amazon.com/dp/B08HDG9JRL
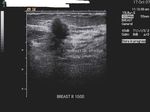
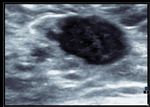
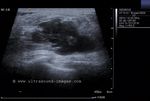
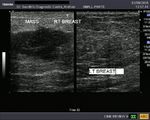
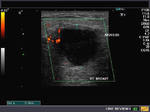
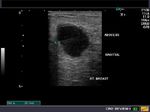
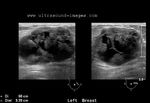
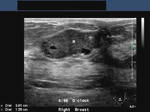
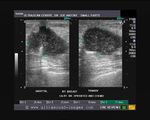
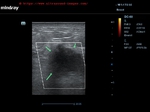
Carcinoma of breast
Malignant lesion of the breast.
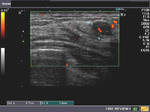
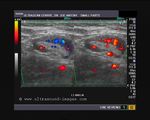
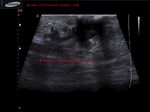
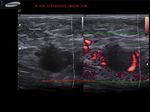
These ultrasound images reveal a hypoechoic, poorly defined, irregular mass in the breast. There is also evidence of acoustic shadowing posteriorly. These findings on sonography suggest malignant mass of the breast. Images courtesy of Dr. Nirmali Dutta, UAE.
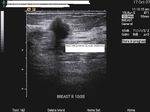
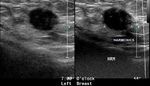
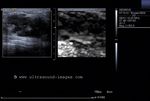
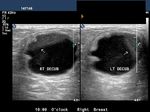
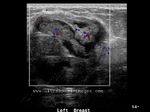
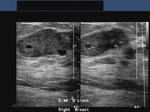
Carcinoma of breast: case-2
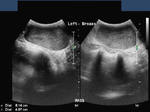
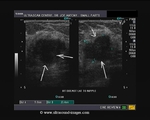
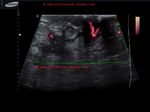
The above ultrasound images show a typical proven case of cancer of the left breast. The tumor is seen as a well defined hypoechoic mass with microlobulation or fine irregularities of the margins. In addition, the mass shows multiple echogenic areas along the rim a clear sign of malignancy in breast carcinoma. Images are courtesy of Ravi Kadasne, MD, UAE
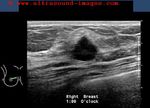
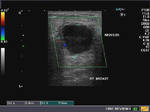
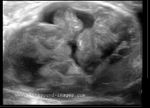
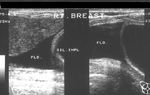
Breast cancer- case-3
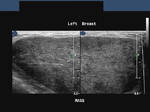
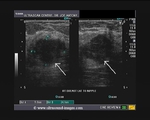
This lady shows a markedly hypoechoic mass of the right breast, that seems to spread vertically (taller than wide), a sign of malignant nature of the breast tumor. In addition, note the presence of fine irregularities of the margin of the lump. All these sonographic findings are suggestive of a breast carcinoma. This ultrasound image is courtesy of Dr. ravi Kadasne, MD, UAE.
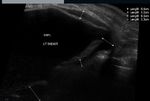
Carcinoma breast -case-4
Ultrasound images of malignant mass left breast
Download this excellent e-book and read in Amazon kindle app on your mobile, tab or Kindle reader:
Atlas of breast ultrasound.
This atlas of sonography of almost every pathology of the breast is presented in Atlas format using the best high resolution ultrasound images.Presented and authored by Dr. Joe Antony, MD
Click here: https://www.amazon.com/dp/B08HDG9JRL
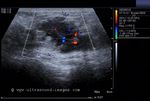
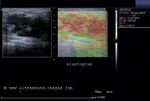
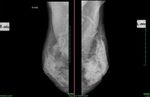
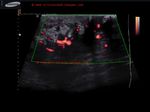
This patient presented with a painful mass in the left breast. Ultrasound images show an irregular mass which is markedly hypoechoic and shows marked rigidity of the tumor tissue on elastography studies. The elastogram image of the breast mass shows red areas which signify possible increase in tumor rigidity suggestive of malignancy. The color Doppler ultrasound image also shows significant increase in vascularity of the breast tumor. The mammography further confirms the presence of a possible malignant tumor in the left breast. This case study is courtesy of Dr. Rahl Patil, MD, India.
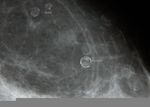
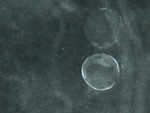
Oil cyst of breast
The breast in this patient showed multiple cystic lesions on sonography. Remarkably, there is acoustic shadowing posterior to the cyst. Clear fluid contents are seen within the cystic lesions. Mammogram of the breast shows rounded lesions with rim calcification, which can explain the acoustic shadowing on sonography. Ultrasound images and mammogram suggest calcific oil cysts of the breast. Oil cysts are produced due to fat necrosis with liquefaction and subsequent cyst formation, usually following trauma. Images courtesy of Dr. Ravi Kadasne, UAE. Ultrasound images taken using a Toshiba Powervision ultrasound scanner.
Reference:
1) http://www.ajronline.org/cgi/reprint/130/6/1189.pdf
2) Sonographic assessment of the symptomatic breast – a pictorial review
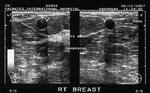
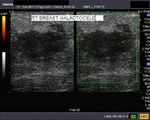
Galactocele of breast
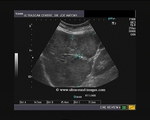
This young female, lactating patient presented with slowly enlarging mass of the right breast. It was non tender and patient had no h/o pyrexia. Sonography of the breast shows a 3 cms. sized hypoechoic (almost cystic) lesion with through transmission. Color doppler images of the breast showed no signficant enhancement of vascularity. These ultrasound images of the breast suggest Galactocele. Galactoceles are formed by cystic dilatation of the lactiferous ducts and contain milk. They are seen in lactating women. Images taken using a Nemio 30 (Toshiba) machine by Dr. Jaydeep Gandhi, Mumbai.
Reference:
1)http://radiology.rsnajnls.org/cgi/reprint/158/1/43.pdf(free article on mammography of galactocele)
2)http://breast-cancer-research.com/content/2/S2/A53
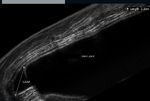
Galactocele with fluid level
This ultrasound image shows a galactocele with a fat-fluid level s/o galactocele. The echogenic material is seen to move with change in posture (arrowed). Sonography done by Dr. Ravi Kadasne, UAE, using a Philips IU 22 ultrasound machine.
Breast Abscess
Ultrasound imaging of the right breast was done on this your lactating female. She presented with pain and swelling of the right breast and underwent drainage of an abscess. The symptoms recurred for which she underwent sonography. Ultrasound images of the breast reveal a rounded, almost anechoic lesion with posterior acoustic enhancement. The lesion measures 2 cms. and has irregular but well defined walls. No internal septae are present. Color Doppler images suggest some increase in vascularity along the rim of the lesion. However, the vascularity may not be prominent due to medication with anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics. These ultrasound findings suggest an abscess of the breast. Another similar lesion is a simple cyst of the breast, which would have well defined but smooth walls. It may also be difficult to differentiate abscess from galactocele of the breast. Carcinoma of breast would appear hypoechoic but not anechoic (as in abscess).
Reference:
1http://www.imaginis.com/breasthealth/ultrasound_images_print.asp
2) http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/781116-diagnosis
Fibroadenoma of breast
This young female patient presented with a palpable, non-tender, freely mobile small mass of the right breast. On sonography of the breast, the mass appeared, oval, measured 10 x 5 mm. and showed smooth margins which were well defined. The lesion was non-calcific and seemed extremely mobile on probe pressure. These ultrasound images are suggestive of fibroadenoma of the breast. The Power Doppler image (bottom right), shows poor vascularity of the lesion.
Reference:
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/345779-imaging
Giant fibroadenoma or Juvenile fibroadenoma
These ultrasound images of the left breast in a 15 yr. old female patient show a large (the mass measured 8.2 cms.), more or less homogenous, well defined mass with posterior acoustic enhancement. These findings suggest a diagnosis of giant fibroadenoma of the left breast. The main differential diagnosis in such a case would be phyllodes tumor. However, phyllodes tumor is seen in females over 30 yrs. of age. Despite the rapid increase in size of the mass, in this case, the potential for malignancy is very low. Ultrasound images are courtesy of Ravi Kadasne, MD, UAE.
Reference:
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/188728-overview
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/345779-overview
Phyllodes tumor of the breast
This 48 year of female patient had a large lump in the medial aspect of the left breast. The ultrasound images of the breast show (above) a large inhomogenous mass of 5.6 x 3.4 cms. with multiple lobulations and cystic spaces also present. The appearance of the tumor was leaf like in its internal architecture. There is also posterior acoustic enhancement.
The images above show minimal internal vascularity on color Doppler ultrasound and 3-D ultrasound (bottom- left), show the internal lobulation with typical leaf like pattern on sonography. The age of the patient, large size of tumor and typical ultrasound features are highly suggestive of this being a Phyllodes tumor of the left breast. Ultrasound images of Phyllodes tumor are courtesy of Ravi Kadasne, MD, UAE.
References:
Fibroadenosis of breast
Benign breast masses:fibroadenosis
This young female patient presented with pain in the right breast and "lumpy feeling" on palpation. Sonography of the right breast showed a hypoechoic, lobulated, well defined mass in the breast. A few anechoic spaces (cystic areas) were also present. Such ultrasound images (appearances) are usually seen in fibroadenosis of the breast. Fibroadenosis is characterized by pain breast with or without palpable masses (lumps). On histopathology, there may be microcysts, fibrosis, adenosis of hyperplastic changes of the breast epithelial tissue. Repeat/ follow up ultrasound would usually show resolution of the mass (usually after 1 to 2 months). It is often difficult to distinguish fibroadenoma from fibroadenosis purely on the basis of sonography alone. (Ultrasound images are courtesy of Dr. Ravi Kadasne, UAE. He used a Philips IU22 ultrasound system here).
Reference:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2429655/?page=1 (free article).
Ultrasound imaging of Breast implant
Case-1:
Breast implants are mainly of two types- the older silicon gel implants and the newer saline implants. The ultrasound image (see case-1) shows the silicon gel implant in the right breast. A small amount of fluid (seroma) is commonly seen around the breast implant for some time after the procedure. Case -2, shows more ultrasound images (panoramic view) with the implant seen as a large hypoechoic sac in the breast. Again some fluid is seen around the implant. This appearance (fluid around the breast implant) may signify the presence of a small leak from the implant. However this patient did not show more specific signs of implant rupture such as radial folds from the implant surface. (Ultrasound images are courtesy of Ravi Kadasne, MD, UAE and Shlomo Gobi, sonographer, Israel).
Reference:
http://radiographics.rsna.org/content/13/6/1323.full.pdf+html(free article and images)- excellent.
Breast seroma following lumpectomy for breast carcinoma
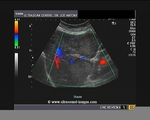
This middle aged female patient had a history of carcinoma of the right breast for which she underwent lumpectomy. Ultrasound image (above left) shows a cystic area in the site of the lumpectomy with echogenic particles within the lesion. real time ultrasound imaging showed considerable motion of the particulate matter in this lesion. This ultrasound feature is typical of seroma of the breast and represents collection of serous fluid and bloody matter within the empty space formed by removal of the breast lump. This is not abnormal and the fluid should be absorbed by the surrounding tissue within a year. However, this was not the only finding in this patient who showed a lump in the left axilla: Ultrasound and color/ Power Doppler images of the left axillary lump show a typical appearance of a solitary enlarged lymph node with marked vascularity along the rim of the node. This appearance suggest either inflammatory lympadenitis (reactive) or more ominously, could mean a metastasis to the lymph node. Tuberculous lymph node involvement typically multiple matted, and hypoechoic nodes with echogenic rim. This node appears to have an echogenic central part with only mild hypoechogenicity of the rim.
References
Article on seroma of breast following lumpectomy for breast cancer
Article on sonographic differentiation of lymph node enlargement
carcinoma breast with liver metastasis
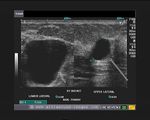
This elderly lady has a solid markedly hypoechoic mass lesion in the right breast, just lateral to the nipple, in the upper lateral quadrant. Ultrasound images of this case show a well defined, non-calcific, mass, which is taller than it is wide and has an irregular contour. These are alarming findings and indicate a possible malignant mass of the right breast.
In addition, the liver shows multiple solid, rounded echogenic mass lesions scattered through both lobes of the liver.
Final diagnosis confirmed by FNAC - carcinoma right breast with liver metastases.
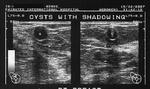
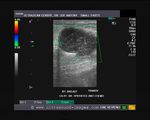
simple breast cysts
This 51-year-old woman presented with right breast lumps. Ultrasound study of the breasts shows 2 cystic lesions measuring 1.5 cm and 4.5 cm in size. The lesions are well defined with thin walls and clear fluid within them. There is evidence of posterior acoustic enhancement and both cysts are aseptate. No evidence of an intramural nodules or debris is present. These ultrasound imaging findings are consistent with simple cysts of the breast. Ultrasound imaging of simple cyst of the breast helps to rule out malignant conditions, and hence further investigations, including mammography may not be indicated. On probe pressure, both cystic lesions appear compressible. This further supports our sonographlc diagnosis of simple cyst of the breast.
carcinoma-breast-with-axillary-node
This elderly lady has a biopsy proven carcinoma of left breast- BIRADS-VI with spread of the cancer locally into surrounding breast tissue and also superficially causing an ulcerating mass just below the nipple. Marked vascularity of the malignant mass is present with prominent vessels within the lesion. There is in additio, an enlarged vascular Lt. axillary lymph node.
Fore more on BIRADS grading of breast cancer:
mastitis-left-breast
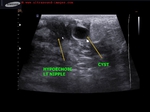
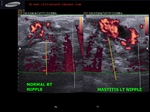
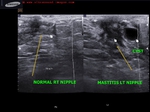
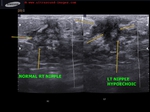
This 12 yr old female child had retracted left nipple with tenderness and pain around the left areola. Ultrasound and color Doppler images show markedly hypoechoic, vascular left nipple (compare with normal Rt. nipple region).
In addition, a simple breast cyst seen lateral to left nipple.
Findings suggest left mastitis or inflammation of left breast.
multiple-juvenile-fibroadenomas-breast
Multiple juvenile fibroadenomas of left breast in a 18 year old female:
- multiple hypoechoic mass lesions left breast
- marked vascularity both peripheral and central with plenty of radial vessels on Power Doppler ultrasound
- these masses can rapidly grow in size giving the term giant fibroadenoma
though they are still benign in nature
- marked cellularity of the masses causes them to be very vascular
- occur in the age group 14 to 22 years
- may be multiple or single masses (in this case were multiple- more than 4 in number)
see more: multiple juvenile fibroadenoma
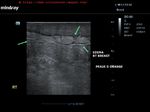
inflammatory-carcinoma-breast
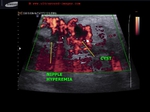
= edematous Rt. breast with peau d'orange appearance
= edematous Rt. upper limb
= hypoechoic mass Rt. breast which shows all characterstics of carcinoma- irregular margins and taller than wide
= peau d'orange (breast pitting edema with orange skin appearance) is associated with lymphatic obstruction and is typically seen in highly infiltrating carcinoma of the breast (called inflammatory breast carcinoma). Inflammatory breast carcinoma is not associated with inflammation. However, appearances of inflammation are present such as severe edema of breast (thus mimic of mastitis).
= Above ultrasound images show typical features of inflammatory carcinoma of breast.
References: Inflammatory cancer of breast