Ultrasound images of diseases of the lungs and pleural cavity
Contents of this page
- Pleural effusion
- Case-2: septate pleural effusion
- Pulmonary consolidation
- Ultrasound image showing Pneumonia or Pneumonic Consolidation of left lung
- Pleural mass
- Normal thymus in neonate
- Large pleural effusion-ultrasound video
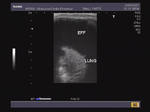
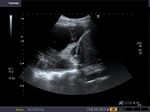
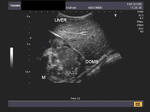
Pleural effusion
Sonography of the chest was done in this patient. Images reveal a large, clear, hypoechoic fluid collection in the left pleural space. The left lung has collapsed into a small mass of tissue compressed by the effusion. A small fibrotic band is seen traversing the fluid. These ultrasound images are diagnostic of pleuraleffusion. Images taken using a Toshiba Nemio 30 color doppler machine, courtesy of Dr. Vikas Arora, Ferozepur, India.
(Advertisement: Download Susan Millar's e-book on a natural approach to treatment of Asthma..)
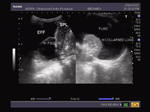
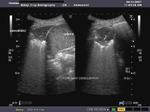
Case-2: septate pleural effusion
The above images (case-2) show a large right pleural effusion with multiple, thick septae. This suggests tuberculous effusion, one of the commonest causes of this kind of pathology. Despite the presence of multiple thick fibrous bands, the fluid appears relatively clear. In the image on bottom row, note the right lobe of liver (to the right of the image). Ultrasound images are courtesy of Gunjan Puri, MD, India.
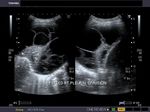
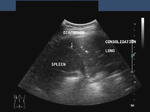
Pulmonary consolidation
Sonography of the left lung reveals loss of normal aeration of the lung parenchyma with echogencity and texture similar to that of the spleen below. The echogenic left dome of diaphragm is seen separating the lower lobe of the lung from the spleen. The normal aerated lung surface would reflect all the sound waves producing a strong shadow. These ultrasound images suggest consolidation of the lung. Image courtesy of Dr. Gunjan Puri, Surat, India. Image taken using a Toshiba Xario, ultrasound and color doppler machine.
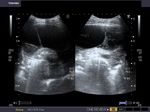
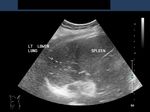
Ultrasound image showing Pneumonia or Pneumonic Consolidation of left lung
>Ultrasound image showing Pneumonia or Pneumonic Consolidation of left lung
This patient also showed symptoms of left sided chest pain and cough with fever. Sonography of left lung shows typical features of consolidation of the left lower lobe. Note the altered echogenicity (soft tissue nature) of the left lower lobe, causing what is called hepatization of the lung (sonographic appearances similar to that of the liver). In some cases of pneumonic consolidation of the lung, it is possible to see fluid or air bronchograms formed by the bronchial tree. In this case there is no evidence of pleural effusion. The echotexture appears heterogenous due to presence of air (echogenic areas) within the consolidated (hypoechoic) lung. Images are courtesy of Dr. Ravi Kadasne, UAE.
Reference:
http://www.journals.elsevierhealth.com/periodicals/ejus/article/PII0929826696001450/abstract
http://content.karger.com/produktedb/produkte.asp?typ=fulltext&file=000100427 (free article and images)
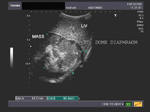
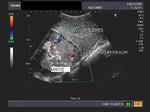
Pleural mass
Solid mass arising from the pleural membrane
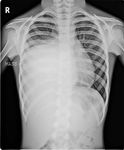
This young female child complained of right sided chest pain. X-ray image shows a large opacity filling the lower half of the right hemithorax with obliteration of right C-P angle. The upper border of the opacity appears convex. Sonography reveals a rounded, large soft tissue mass just above the right dome of diaphragm, measuring approximately 8 x 7 cms. Color doppler imaging shows vessels feeding the lesion. The right dome of diaphragm appears to be compressed with pressure effect on the right lobe of liver. These ultrasound images suggest right pleural or pulmonary mass, possibly malignant.
Images courtesy of Dr. Jaydeep Gandhi, Mumbai, India. He used a Toshiba, Nemio 30 color doppler machine.
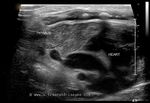
Normal thymus in neonate
The normal thymus is located posterior to the sternum in the superior mediastinum, anterior to the great vessels of the thorax. The thymus is seen on ultrasound (see image above), as a hypoechoic gland (more hypoechoic than thyroid) and shows a slightly grainy texture. The normal thymus also shows few linear strands within it due to fine fibrous capsular septae/ compartments within it. In the neonate, the normal thymus may vary in size and may extend below up to the diaphragm and above till the neck. In certain cases, the neonatal sternum may show a defect through which part of the thymus may herniate. The margins of the thymus are well defined due to the fibrous capsule. This sagittal section ultrasound image of thymus is courtesy of Dr. Ravi Kadasne, MD, UAE.
References: Normal thymus- sonographic features (radiographics article- RSNA)