Salivary glands
Contents of this page
- Sonography of the normal salivary glands
- Parotitis
- Warthin's tumour (cystadenolymphoma)
- Case-2: Warthin tumor of the right parotid gland
- Parotid abscess
- Sialolithiasis: Salivary gland calculus
- Case-2: Left Wharton duct calculus
- Cystic lesion of parotid salivary gland
- Parotid gland Schwannoma
- pleomorphic-adenoma-parotid
- chronic-parotitis
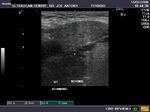
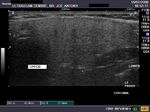
Sonography of the normal salivary glands
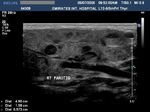
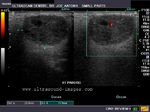
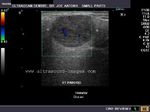
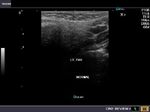
A) Submandibular salivary glands
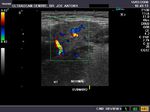
The above ultrasound images of the normal submandibular salivary glands show homogenous echotexture and fine soft tissue echogenicity. The color doppler image shows the gland to be vascular. Echogenicity appears slightly less than that of a normal thyroid gland.
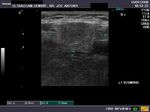
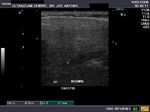
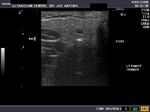
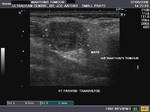
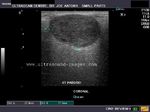
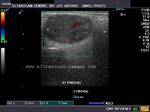
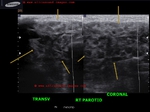
B) Parotid gland
The normal parotids.
The parotid gland is much larger than the submandibular salivary gland. Its transverse diameter is considerably smaller than the coronal dimensions. The parotidshows almost the same texture and echogenicity as the submandibular gland.
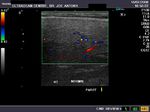
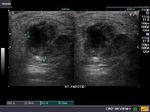
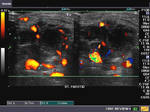
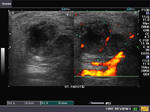
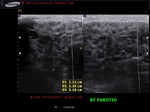
Parotitis
Sonography of the parotid glands in this patient reveal: a) bilateral microabscess formation with b) swollen glands c) hypoechoic lesions. These ultrasound images suggest inflammation s/o parotitis. Sonographic images taken using Philips iU22 machine by Dr. Ravi Kadasne, UAE.
Reference: http://www.emedicine.com/ent/topic600.htm(free article and images)
Warthin's tumour (cystadenolymphoma)
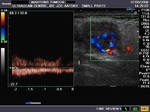
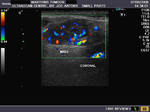
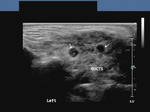
Sonography of salivary gland mass.
This 50 yr. old male patient complained of swelling and pain in the region of the parotid glands on both sides. Sonography of the parotid glands revealed 1) bilateral hypoechoic, well defined masses (larger on the right side) which show no significant acoustic enhancement. 2)The lesion in the right parotid measures 2.5 x 1.6 x 1.2 cms. and that on the left side measures 0.7 cms.3) Fine septae are seen within the masses. 4) Color doppler imaging shows multiple vessels within the mass with typical low velocity flow. These findings suggest either pleomorphic adenoma of the parotids or Warthin's timour. Absence of posterior acoustic enhancement in these ultrasound images suggests that this is a Warthin's tumour of the parotid gland. Histopathological study confirmed this to be Warthin's tumour.
Ultrasound images taken by Joe Antony, MD, using a Toshiba Nemio- XG color doppler machine.
Reference: http://bjr.birjournals.org/cgi/content/full/76/904/271( free article and images).. excellent
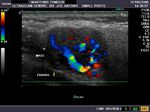
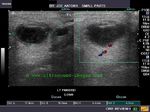
Case-2: Warthin tumor of the right parotid gland
The above sonographic images of the right parotid gland show an obvious well defined, hypoechoic mass within the middle third of the gland in this middle aged male. Measuring 2.7 x 1.8 cms., the mass shows mild posterior acoustic enhancement (a feature of pleomorphic adenoma). Power Doppler image shows few vessels within the mass.
Color Doppler images of the tumor in the right parotid gland show mild vascularity of the mass. There is no evidence of calcification, but a few cystic areas are present within the mass. The diagnostic possibilities in this case are Warthin tumor versus pleomorphic adenoma of the right parotid gland. The possibility of Warthin tumor is more likely considering the various features seen in these ultrasound images.
References: http://radiographics.rsna.org/content/26/3/745.full.pdf+html (free article- excellent).
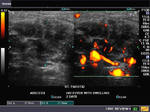
Parotid abscess
Sonography of the parotid gland s was done in this 2 yr. old child, to evaluate a swelling in the right parotid region. Ultrasound and Power Doppler / Color Doppler images reveal: a) Marked swelling of the right parotid gland b) multiple anechoic and hypoechoic cystic spaces within the right parotid gland c) marked augmentation of vascularity in the right parotid gland. These ultrasound images suggest right parotid abscess. The child had earlier episodes of pain and swelling in this region. The left parotid gland appears normal.
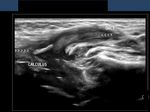
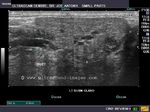
Sialolithiasis: Salivary gland calculus
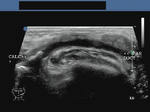
a) Calculus (stone) in parotid duct (Stensen's duct)
This elderly female patient presented with pain and swelling in left parotid region. Sonography of the left parotid gland showed an enlarged parotid gland with dilated branches of the parotid duct (see ultrasound image on top left). The left parotid duct (Stensen's duct) appeared markedly dilated with a calculus in the terminal part of the duct (images on top-right and bottom left). The 3-D ultrasound image (bottom right) shows the calculus (stone) in Left Stensen's duct (parotid duct). Sialolithiasis of the parotid duct is relatively rare with most calculi of salivary gland (90 %) being located in the submandibular salivary gland duct (Wharton's duct). If not removed in time, the complications include obstructive sialadenitis (inflammation) and atrophy of the salivary gland. Ultrasound images of sialolithiasis (calculus in Parotid duct) are courtesy of Dr. Ravi Kadasne, UAE.
Reference:
1) http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/484955_2 (free article) 2) http://www.fpnotebook.com/ENT/Salivary/Slths.htm (free article)
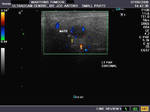
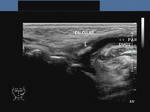
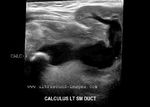
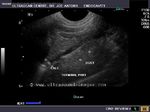
b) Sialolithiasis: Calculus in left Wharton duct
(Stone in left submandibular duct)
This 3D multiplanar reconstruction ultrasound image shows a large calculus (stone) in the left submandibular duct (Wharton duct), close to its opening under the tongue (the sublingual caruncle). This orifice is close to the sublingual salivary gland. The Wharton duct calculus (CALC) is seen as a markedly hyperechoic linear structure within the dilated duct of the left submandibular salivary gland. Note also the dilatation of the intraglandular part (within the submandibular gland) of the Wharton duct. Chronic obstruction can cause infections and subsequent atrophy of the submandibular salivary gland, if left unresolved. Ultrasound image of Wharton duct calculus is courtesy of Dr. Ravi Kadasne, MD, UAE.
Reference: http://radiographics.rsna.org/content/26/3/745.full.pdf+html (free article on Salivary gland ultrasound).
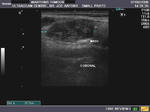
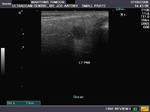
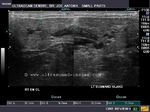
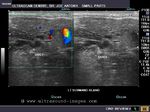
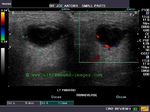
Case-2: Left Wharton duct calculus
Enlarged left submandibular gland
This patient presented with typical symptoms of sialolithiasis of the left salivary gland. Ultrasound images show changes in the left submandibular salivary gland like hypoechoic gland parenchyma and a markedly dilated Wharton duct as it emerges from the gland. Using the transvaginal probe we could visualize the stone in the terminal part of the Wharton duct. The possibility of the Wharton duct being a vessel was excluded by using color Doppler imaging.
Reference: http://ultrasound-videos.blogspot.com/2011/08/sonography-of-wharton-duct-calculus.html Ultrasound video of this case and blog article.
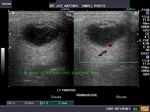
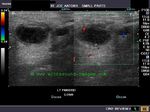
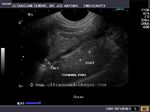
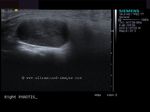
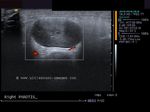
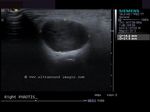
Cystic lesion of parotid salivary gland
This elderly male patient showed a swelling of the left parotid gland. Ultrasound images of the case are shown below. They show an obviously anechoic lesion with comparatively smooth walled margins. On increasing the gain further, there appear to be few scattered fine particles within the cystic lesion in the left parotid salivary gland. No internal vessels are seen inside the lesion again confirming its cystic nature.
Further ultrasound imaging showed that there is another smaller lesion just below the larger cystic area. Thus the left parotid gland has two cysts within its tissue. A rim of few vessels suggest poor vascularity around the cyst. There is also evidence of posterior acoustic enhancement again suggestive of a cystic nature of the lesions. The commonest cause of such an appearance can be retention cysts of the parotid salivary gland. The other diagnostic possibilities include - cystic changes within a pleomorphic adenoma or cystic degeneration of a Warthin's tumor. Such cysts are also seen within degenerative (cystic) changes in lymph nodes. This patient has no history of pain nor was there any tenderness over the lesion ruling out parotid abscess as a possibility. Thus the possibilities in this case appear to be a cystic lesion or cystic changes of a benign tumor of the salivary gland.
References: http://radiographics.rsna.org/content/26/3/745.full.pdf (excellent free article and images)
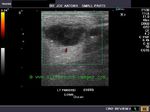
Parotid gland Schwannoma
This elderly patient showed a gradually enlarging mass of the right parotid area. Sonography of the right parotid gland showed a 14 x 22 mm. hypoechoic, well defined mass within the parotid gland. It showed a homogenous and well encapsulated appearance. These ultrasound images favor a diagnosis of a benign tumor of the parotid salivary gland. Biopsy of the mass showed it to be Parotid gland Schwannoma (the tumor having arisen from the facial nerve within the parotid). Ultrasound and other imaging methods may not be able to accurately differentiate Schwannoma from other parotid tumors. Ultrasound images of parotid schwannoma is courtesy of Mr. Shlomo Gobi, Israel.
References: http://eng.hi138.com/?i241570_Ultrasound_parotid_gland_schwannomas_Misdiagnosis
pleomorphic-adenoma-parotid
Left parotid mass of few months duration on FNAC proved to be pleomorphic adenoma.
Typical sonographic findings of pleomorphic adenoma:
- hypoechoic mass usually of parotid salivary gland
-usually single ( solitary)
- homogenous mass or mild inhomogeneity
- posterior acoustic enhancement present
- poor vascularity
- little or no cystic areas usually
The solitary occurrence and posterior acoustic enhancement help favor a diagnosis of pleomorphic adenoma as opposed to Warthin's tumor
References: sonography of pleomorphic adenoma
ultrasound imaging of pleomorphic adenoma
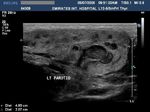
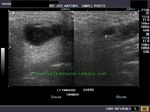
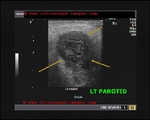
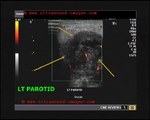
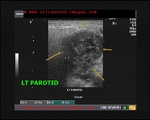
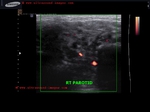
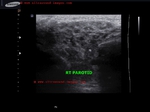
chronic-parotitis
This 20 year old female patient had multiple patchy hypoechoic lesions throughout the Rt. parotid salivary gland (see ultrasound images above). Mild increase in vascularity is also present.
A few calcific foci also noted.
Similar changes were also seen (lesser degree) in left parotid salivary gland.
Findings suggest parotitis of chronic nature (patient had repeated attacks of parotid pain)