Metabolic Diseases
Contents of this page
- Normal liver
- Diffuse fatty change of liver
- Diffuse fatty liver with focal fatty sparing
- Focal fatty change of liver
- Cirrhosis of liver with portal vein thrombosis
- early-cirrhosis-liver-case-2
- Grading-of-fatty-liver-or-hepatic-steatosis
- cirrhosis-liver-3D-ultrasound
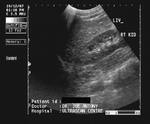
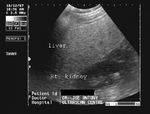
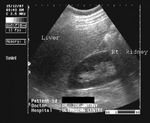
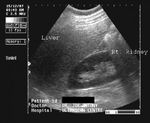
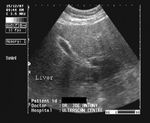
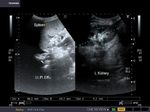
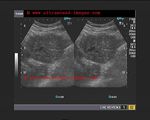
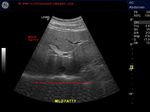
Normal liver
In this sonographic image, note the normal echogenicity of the liver which is almost isoechoic with the parenchyma of the right kidney.
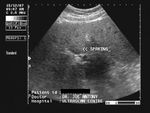
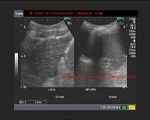
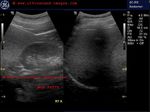
Diffuse fatty change of liver
In this ultrasound image of the liver there is diffuse increase of liver echogenicity. The liver appears markedly hyperechoic as compared to renal cortex.
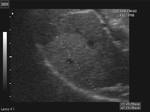
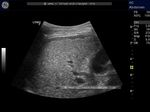
Diffuse fatty liver with focal fatty sparing
In these 3 ultrasound images there is diffuse fatty change of liver with focal fatty sparing in the periportal region, just anterior to the porta hepatis. This is a typical site of focal fatty sparing. This is seen as a small hypoechoic region. Images taken with a Pie Scanner 100 Falco, by Dr. Joe Antony.
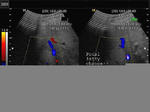
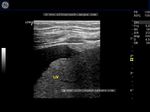
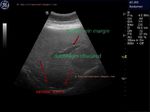
Focal fatty change of liver
The above ultrasound image (left) shows a hyperechoic lesion of 4 x 3 cms. in the periphery of right lobe of liver. Color doppler scan shows absence of mass effect (vessels are not displaced by the lesion). This suggests focal fatty change of liver. Such lesions may change rapidly over time. Images taken using a Medison SA 8000 color doppler machine, courtesy of Dr. Arun Mahajan, Delhi, India.
Reference:
1) http://www.emedicine.com/med/topic775.htm(free article-excellent)>
2) Focal fatty change(free article and images)
3) Focal fatty change of the liver, a hitherto poorly recognized entity. (interesting insight into the causes of focal fatty change of liver)
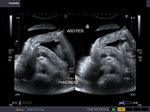
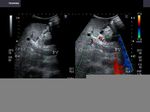
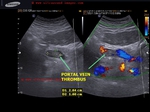
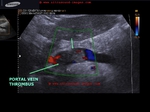
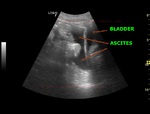
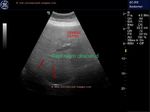
Cirrhosis of liver with portal vein thrombosis
cirrhosis-liver-portal-vein-thrombus-case-2
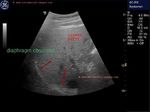
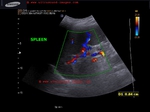
This patient presented with distension of abdomen. Sonography of the abdomen showed: a) large ascites (fluid collection inside the peritoneal cavity). The anechoic fluid is seen surrounding the liver and the kidneys. b) There is also a moderate collection of fluid in the pleural cavity (pleural effusion). This is seen as fluid just above the diaphragm. c) Nodularity of the liver is present. This is seen as irregular surface of the right and left lobe, well outlined by ascitic fluid. d) There is also coarse echotexture of the liver with increased echogenicity. e) There is also relative increase in size of the left lobe of liver- the so-called volume redistribution in the size of liver. f) Lastly, Color Doppler imaging shows a thrombus in upper portal vein which appears moderately dilated (14.5 mm.). There is also evidence of splenomegaly . These ultrasound images are diagnostic of cirrhosis with portal vein thrombosis. Images courtesy of Gunjan Puri, MD, India.
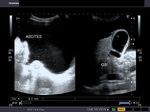
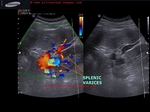
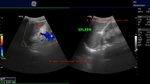
Case-2:
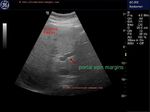
A large echogenic thrombus seen in dilated portal vein.
The cause of this kind of portal vein thrombus is usually sluggish flow in the vessel- a common association of cirrhosis of liver.
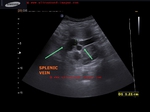
also: splenomegaly and splenic varices seen.
Reference: Sonography in cirrhosis of liver (free article and images).
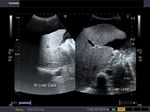
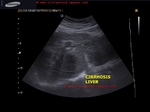
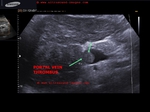
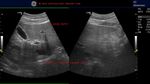
early-cirrhosis-liver-case-2
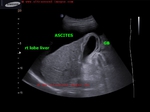
This male patient aged 70 years is a chronic alcoholic. Ultrasound images show early cirrhotic changes of the liver with nodularity of the margins of the liver appreciated best on high frequency scan of the liver surface (linear probe). There is also associated mild splenomegaly and moderate ascites. Point: When in doubt about the nodularity of the liver the use of high frequency probe helps clinch the diagnosis with even early changes of cirrhosis evident as in this case
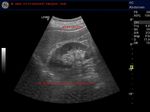
Another-case-of-nodular-cirrhosis
This is another case of alcoholic cirrhosis with all the features of cirrhotic liver including nodular surface of liver and ascites. it may be difficult to distinguish alcohol induced cirrhosis from non alcoholic cirrhosis on sonography alone. History, is thus important.
Grading-of-fatty-liver-or-hepatic-steatosis
Hepatic steatosis or fatty liver is graded from mild (grade-1) to moderate (grade-2) to severe (grade-3). The normal liver parenchyma is slightly less echogenic or almost the same echogenicity as the spleen. The hepatic echogenicity is about the same as then renal cortex.
In mild fatty liver (grade-1): the liver echogenicity is greater than the renal cortex. However, the periportal echoes are well defined and the diaphragm is not obscured. (see ultrasound images above).
In moderate fatty liver (grade-2): liver echogenicity is greater than renal cortex. Also, periportal echoes are not visualized well. But the diaphragm is well imaged.
In severe fatty liver (grade-3): periportal echoes are obscured as well as poorly defined diaphragm outline. (see sonographic images above).
References: Ultrasound grading of fatty liver or hepatic steatosis
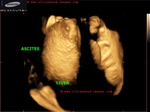
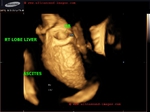
cirrhosis-liver-3D-ultrasound
3D ultrasound with surface rendering shows the Rt. lobe of liver-
-contracted shrunken liver s/o end stage cirrhosis
- nodular cobblestone surface of liver on 3D accentuated by surrounding ascitic fluid
- splenomegaly with splenic varices s/o portal hypertension