Ultrasound images of fetal general
Contents of this page
- Normal fetal anatomy
- IUFD-intrauterine-fetal-death
- Fetal club hand deformity
- How to spot the Normal ductus venosus:
- Color doppler imaging of fetal growth retardation (IUGR) and fetal hypoxia
- Color Doppler imaging of the uterine artery
- fetal hydrops or hydrops fetalis
- icthyosis in fetus
- icthyosis in fetus- case-2
- fetal clubfoot
- fetal anemia
- dolicocephaly-fetal
- Fetal-polydactyly-foot
Normal fetal anatomy
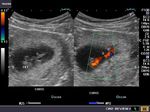
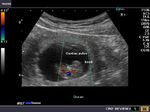
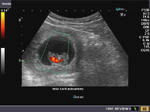
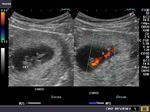
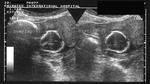
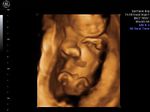
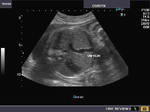
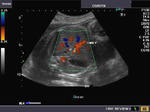
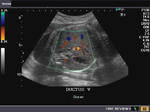
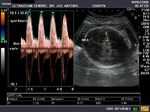
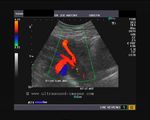
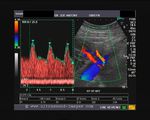
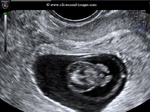
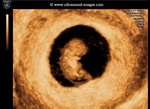
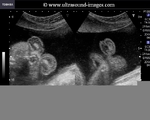
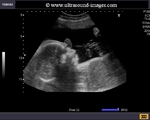
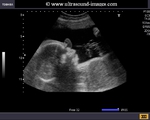
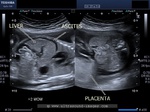
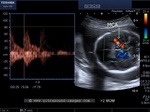
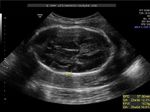
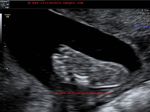
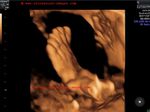
Sonographic anatomy of 9 week old fetus
These ultrasound images show a normal early fetus of 9 weeks gestational age (1st trimester) and are taken via the transabdominal route. Among the structures seen are the fetus with the bulkier head (cephalic part) and the fetal heart on Color Doppler and Power Doppler imaging. Spectral Doppler waveform (Topmost row- right) shows the cardiac pulsations with heart rate. The fetal cardiac pulsations are also well visualized in the Power Doppler image of the fetus (2nd row from bottom- Right). The amniotic membrane (amnion) is also well visualized as it covers the fetus and is well clear of the gestational sac (Topmost row -left). At a later date, the amnion merges with the gestational sac and would not be visualized. The early umbilical cord is also visualized as it extends from the fetus to the uterine wall
(ultrasound/ Doppler image on bottom row).
Download my E book for Amazon Kindle (download free Kindle reader for i Phone or Android)
Assorted ultrasound cases- by Joe Antony, MD
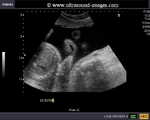
IUFD-intrauterine-fetal-death
This ultrasound image of the fetal skull reveal overlap of the bones of the calvarium following fetal demise. This is known as the Spalding sign and is diagnostic of intrauterine fetal death. Image courtesy Dr. Ravi Kadasne, UAE.
case-2 Ultrasound video of fetal demise in 2nd trimester pregnancy
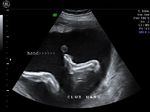
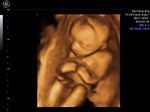
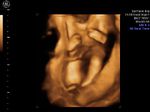
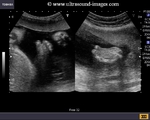
Fetal club hand deformity
This 2nd trimester fetus shows short forearm bone (radius) with radial deviation of the wrist. The image 1st (top left) is a B-mode ultrasound image showing this deformity of the hand. The other 3 images are 3-D (3 dimensional) ultrasound images showing the same anomaly in this fetus. These ultrasound images suggest fetal radial club hand anomaly. Radial club hand is the commonest fetal club hand anomaly. It is important to look for other fetal malformations as this anomaly is usually not isolated. Ultrasound images courtesy of Dr. Dilraj Gandhi, India.
Reference: http://www.wheelessonline.com/ortho/radial_club_hand
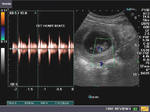
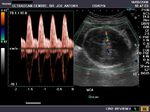
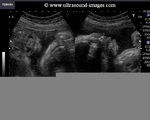
How to spot the Normal ductus venosus:
It is often difficult to spot the ductus venosus among the numerous vessels in the fetal abdomen. I have devised an easy way out. a) First spot the umbilical vein passing through the fetal abdomen. b) Switch on the color Doppler function to view the flow of the umbilical vein. c) Reduce or increase the PRF (pulse repetition frequency) function of the color flow until you spot a prominent but short vessel with MARKED ALIASING (ie: turbulent flow producing a multiple shades in the flow image). This is most likely to be the ductus venosus. Note the location of the vessel, just anterior to the fetal aorta. d) Now switch on the spectral doppler trace of the vessel. This will give a wavy spectral waveform with 3 waves (d): The S wave, the D wave and the A wave. Note the marked diastolic flow in this waveform. This is diagnostic of a normal Ductus venosus.
All images by Joe Antony, MD, using a Toshiba Nemio -XG ultrasound system.
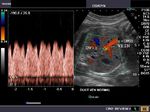
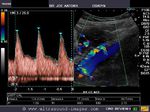
Color doppler imaging of fetal growth retardation (IUGR) and fetal hypoxia
Doppler of umbilical artery
Color doppler and spectral waveform imaging of the umbilical artery shows reversal of diastolic flow. This is an ominous sign of fetal compromise/ hypoxia and requires us to evaluate the fetal middle cerebral artery and ductus venosus. The diastolic flow reversal in umbilical arteries signifies severe placental insufficiency and increased placental vascular resistance, which is bad news for the fetus.
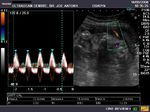
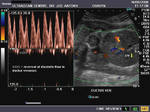
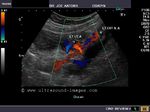
Doppler evaluation of the MCA (middle cerebral artery)
Color doppler and spectral waveform of the middle cerebral artery shows increased diastolic flow in the fetal brain suggesting a "fetal brain sparing" effect, whereby, the fetal cerebral vessels "open up", lowering the cerebral vascular resistance to increase flow to the brain thus diverting blood to the important organs in a state of overall fetal hypoxia.
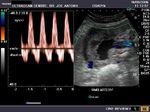
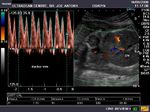
Doppler evaluation of the Ductus Venosus (DV)
Doppler spectral waveform of the ductus venosus shows not just absent diastolic flow, but actual flow reversal during diastole. This is an ominous sign and suggest severe fetal compromise (ie: hypoxia). It is associated with very high fetal morbitidity and mortality. In this fetus, the Resistance Index for the vessels in this case are as follows:
Umb. Artery: 0.92 ; MCA: 0.75; DV: 0.99
The cerebro-placental ratio = RI (mca)/ RI (umb. a.) = 0.75/0.92 = 0.81.
The normal ratio is > 1. This suggests severe fetal growth retardation (IUGR) in this fetus possibly due to severe placental insufficiency. Ultrasound imaging and biometry also confirmed evidence of growth retardation in this fetus (28 weeks by ultrasound versus 31 weeks by Last Menstrual period). All these ultrasound and color doppler images suggest fetal growth reardation with fetal compromise and anoxia- meaning we have a very sick fetus that needs prompt delivery.
Images taken by Joe Antony, MD, using Toshiba, Nemio- XG Color doppler machine.
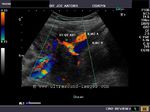
Color Doppler imaging of the uterine artery
14 week pregnancy
The color Doppler ultrasound images above show the uterine arteries on either side in a 14 week old pregnancy. The technique of tracing the uterine artery is described at:
http://ultrasound-videos.blogspot.com/2011/07/color-doppler-ultrasound-and-spectral.html
The spectral waveform of the right uterine artery shows a normal early diastolic notch which is normally seen till the age of 25 weeks of gestation.PI and RI values early in the pregnancy can be quite high signifying increased resistance in the placental and chorionic vascular beds. Thus PI values are typically higher than 2.5 in 11 to 14 week period, decreasing gradually as the gestation progresses. However, PI and RI values can vary depending on placental position (with low PI values in the uterine artery on the side of the placenta). Persistence of the diastolic notch and high PI and RI values can signify danger of the pre-eclampsia, placental abruption and PIH (pregnancy induced hypertension ), and IUGR. Thus uterine artery doppler can be used to predict or exclude danger to the fetus in the coming months.The left uterine artery in the color Doppler image above is smaller in size due to the placenta being more on the right side of the uterus.
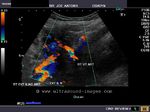
Uterine artery in 24 week pregnancy
The right uterine artery in the color Doppler ultrasound image (top- left) shows bifurcation or division just before it crosses the right external iliac artery and vein. This was a 24 week old pregnancy. The spectral Doppler ultrasound image on right shows normal low resistance flow typically seen at this stage of pregnancy. Video clip of this case can be seen at:
color Doppler video clip of bifurcated uterine artery
The RI of the uterine artery in this case measures 0.51, well within the normal limits.
References: Anatomical variants of uterine artery
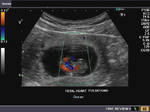
Fetal hydrops or hydrops fetalis
This is the case of a 10 week old fetus which was imaged via transvaginal route. Ultrasound images of the fetus show generalised subcutaneous oedema or anasarca along with small pleural effusions bilaterally.
There is also evidence of mild polyhydramnios. These ultrasound findings are typical of Fetal hydrops or hydrops fetalis as it was earlier called. The 3-D ultrasound image of this fetus is seen at the extreme right. It shows evidence of the generalised anasarca from a 3-D surface rendering perspective.
It is both unusual and difficult to diagnose Fetal hydrops or hydrops fetalis as such an early stage of pregnancy, in the first trimester.
(Ultrasound images of Fetal hydrops are courtesy of Dr. Mayank Chowdhury, MD, India)
References:
1. Sonoworld article on Fetal hydrops
2. Free article on ultrasound imaging in Fetal hydrops
Icthyosis in fetus
Icthyosis is a severe and very rare congenital anomaly seen in foetuses where there is marked thickening of the keratin in the skin resulting in certain typical appearances in the fetus. It can very often be lethal though there are reports of infants with icthyosis surviving to young adulthood. Icthyosis is also called Harlequin Icthyosis because of its typical appearances. Icthyosis means fishlike appearance due to the resemblance of the fetus to a fish. These ultrasound images show typical features of Harlequin Icthyosis:
1- bilateral ectropion resulting in bulbous orbits due to the eversion of the eyelids. The fetus in these ultrasound images shows bilateral orbital masses due to ectropion.
2-eclabion or eversion of the lips resulting in a constantly open mouth. After repeated imaging over a period of time, the mouth remained open all the time.
3- fixed flexion deformity of the limbs is a typical feature of Icthyosis
4- fusion of the digits is also seen in these ultrasound images
5- flat nose is also another feature seen in these images
6- often there is markedly echogenic amniotic fluid- not seen in these ultrasound images
These ultrasound images of Harlequin Icthyosis are courtesy of Dr Durr-e Sabih, FRCP, Pakistan.
References: free articles and images of sonography of Harlequin Icthyosis
http://www.jultrasoundmed.org/
Icthyosis in fetus - case-2
Another case of icthyosis - this time note the prominence of the tongue, in these ultrasound images, (macroglossia), protruding through the open mouth.
A snap of the aborted fetus is also shown, showing the thick plate like skin, resembling scales of a fish or a little more like the skin of a rhino (that is what it looks like to me). The resultant appearance of the fetus can be quite shocking for the parents. These ultrasound images are also courtesy of Dr. Durr-e-Sabih, FRCP.
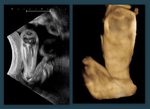
Fetal clubfoot
Fetal clubfoot or congenital talipes equinovarus anomaly is characterized by the foot being inverted and rotated medially. This results in the dorsum of the foot being rotated medially with the ultrasound images showing the metatarsals and phalanges of the affected foot in the same view and same plane as the tibia and fibula of the lower leg. This also results in the foot having a club like appearance and is called club foot or congenital talipes equinovarus.
The 3D ultrasound image above shows fetal clubfoot in 3D surface rendering and is courtesy of Dr. Ravi Kadasne, MD, UAE.
References:
Fetal club foot- ultrasound imaging
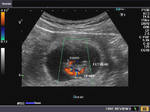
Fetal anemia
This 23 week fetus shows multiple abnormal findings:
1. there is evidence of mild ascites with fetal hepatomegaly.
2. The placenta appears moderately thickened.
3. The fetal middle cerebral artery peak systolic velocity (or PSV) measures 81 cm/s. This is abnormal as the normal peak systolic velocity at 23 weeks gestation has a mean value of approximately 30 cm/s. The measured value, thus exceeds more than 2.0 multiples of median, which is abnormal. Any MCA peak systolic velocity greater than 1.5 multiples of median (MoM) indicates possible fetal anaemia.
Other ultrasound findings, which may be present in fatal anaemia include-fetal hydrops and splenomegaly. The angle of insulation while measuring the MCA peak systolic velocity should be as close to 0 degrees as possible.
All these ultrasound and colour Doppler image findings suggest the presence of fetal anaemia. these ultrasound images of fetal anaemia are courtesy of
Durr-e-Sabih, FRCP.
References:
1. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/uog.6436/pdf
2. ultrasound diagnosis of fetal anaemia
3. sonography of fetal anaemia
Dolicocephaly-fetal
This 3rd trimester fetus shows a markedly elongated fetal calvarium with a reduction of the bi- parietal diameter (BPD) and a simultaneous increase in the anterior posterior (AP) diameter also known as the fronto occipital diameter. this has resulted in a boat shaped skull a condition called the as dolicocephaly. This condition, dolicocephaly is not usually associated with any syndromes or other congenital anomalies and can be considered as a normal variant in skull shape.
This ultrasound image of dolicocephaly is courtesy of Mayank Chowdhury, MD.
References:
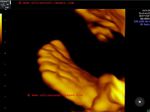
Fetal-polydactyly-foot
The above B mode and 3D ultrasound images show polydactyly of the the fetal foot in a 22 week old fetus. Sonographic images of polydactyly are courtesy of Dr. Firoz Bhuvar, MD, India. In this case, there are 6 fetal toes instead of the normal 5 digits. Fetal polydactyly may be pre-axial or post-axial. Post-axial polydactyly is usually an isloated finding with no associated chromosomal anomalies in the fetus. However, pre-axial polydactyly may usually be associated with syndromes such as HOLT- ORAM sydnrome, carpenter syndrome and VACTERL. Most cases of polydactyly are post-axial. Careful assessment of the fetus is mandatory on all cases of polydactyly.
References: Ultrasound imaging of polydactyly in fetus