Ultrasound images of lesions of gall bladder wall
Contents of this page
- Segmental adenomyomatosis of gall bladder
- Diffuse adenomyomatosis of gall bladder
- Case-2: Diffuse adenomyomatosis of gallbladder
- Tiny polyp of the gall bladder wall
- Large gall bladder polyp
- Multiple gall bladder polyps
- Acalculous Cholecystitis
- Acute cholecystitis- case-2
- Calculous cholecystitis
- Chronic cholecystitis
- 3D ultrasound imaging of gallbladder polyps
- gallbladder-wall-thickening-dengue
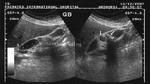
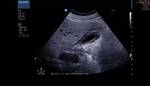
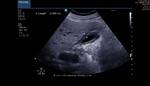
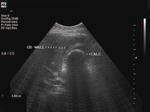
Segmental adenomyomatosis of gall bladder
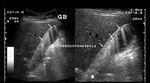
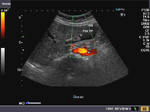
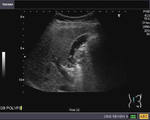
This patient underwent routine sonography of the abdomen. Ultrasound images of the gall bladder reveal thickening and constriction of the mid segment dividing the lumen into a fundic area and another part towards the neck. There is also evidence of small calculi in the fundic segment of the gall bladder. These ultrasound images suggest segmental adenomyomatosis of the gall bladder. Adenomyomatosis of the gall bladder may be segmental, diffuse or fundal. Images taken using Toshiba Powervision ultrasound and color doppler machine, courtesy of Dr. Ravi Kadasne, Al Ein, UAE.
Reference:Segmental adenomyomatosis of gall bladder
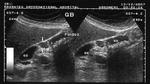
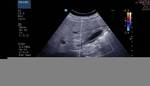
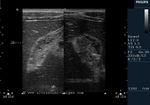
Diffuse adenomyomatosis of gall bladder
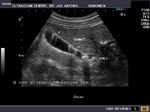
These gall bladder ultrasound images show multiple echogenic foci within the GB wall with V-shaped comet-tail artefacts. There is also diffuse thickening of the gall bladder wall. The comet tail artefacts are the result of minute cholesterol calculi within small sinuses or diverticuli (Rokitansky -Aschoff sinuses) in the Gall bladder wall. These findings suggest adenomyomatosis of the gall bladder. Ultrasound images are courtesy of Dr. Ravi Kadasne, UAE.
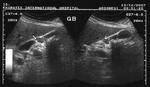
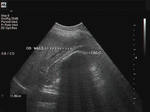
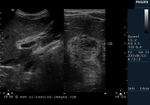
Case-2: Diffuse adenomyomatosis of gallbladder
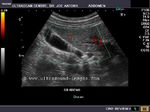
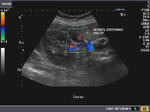
This middle aged male has many of the typical ultrasound features of diffuse adenomyomatosis of the gallbladder. Adenomyomatosis is also known as adenomyomatous hyperplasia of the gall bladder, and this case shows the diagnostic findings of gallbladder wall thickening with multiple echogenic foci within these walls. The Power Doppler ultrasound image shows no other features. Note the associated finding of cholelithiasis (a gall bladder calculus (9mm.) present in the GB neck). Studies show that cholelithiasis may be associated with diffuse adenomyomatosis of the gallbladder.
Reference: free article on radiology of adenomyomatosis
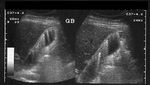
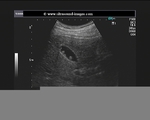
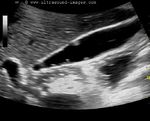
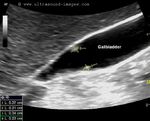
Tiny polyp of the gall bladder wall
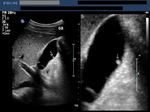
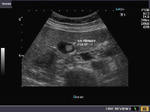
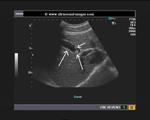
Small gall bladder polyp. This ultrasound image shows a small polyp of the inferior wall of the gall bladder. Note the small base of the polyp, suggesting its benign nature. Such polyps are usually the result of chronic inflammation. Ultrasound image courtesy of Dr. Ravi Kadasne, UAE. He used a Philips IU22 machine to obtain this image.
Reference: http://www.emedicine.com/MED/topic2711.htm
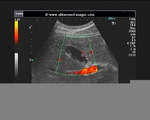
Large gall bladder polyp
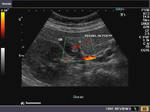
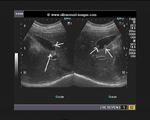
This middle aged, female, patient had non-specific symptoms for which she underwent routine sonography of the abdomen. Ultrasound, Color Doppler and Power Doppler images of the gall bladder reveal an echogenic, oval, smooth walled solid lesion in the gall bladder lumen. It appears attached to the upper wall of the gall bladder, though some movement was present on real time imaging. Color Doppler images show a vessel, clearly seen entering the mass from the upper wall of the gall bladder. These ultrasound images are diagnostic of gall bladder polyp. Such polyps need to be followed up for increase in size and changes which may suggest malignant transformation. Images taken by Joe Antony, MD, India, using a Toshiba Nemio-XG ultrasound system.
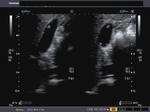
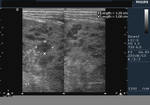
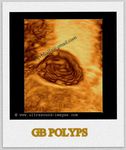
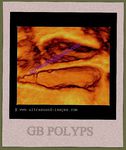
Multiple gall bladder polyps
case-1 case-2
These images show multiple, small polyps of the gall bladder (different patients). Ultrasound image on left is courtesy of Dr. Durr-e-Sabih, Pakistan. Image on right is courtesy of Dr. Gunjan Puri, MD, India.
another example of multiple gall bladder polyps
This young male patient (see ultrasound images above) also has multiple gall bladder polyps ranging in size from 4 to 8 mm. Such an ultrasound finding of multiple or solitary polyps of the gallbladder is usually incidental with most such patients being asymptomatic. However, the presence of multiple or larger gallbladder polyps should make the sonographer look for vascularity or feeder vessels supplying the polyps. In these ultrasound and Power Doppler images, the gallbladder polyps donot show any significant vascularity suggesting a more benign nature. Follow up sonography must be done to look for changes in size or ultrasound features that may indicate malignant transofrmation.
Acalculous Cholecystitis
This patient had severe pain in right hypochondrium and pyrexia. The total leucocyte count was markedly elevated (38000). Sonography of the liver and spleen showed multiple patchy hypoechoic lesions suggestive of multiple minute abscesses. The gall bladder was markedly distended with thickened and edematous wall. Color Doppler imaging (not shown here), revealed increased vascularity of the gall bladder wall. Note absence of GB (Gall Bladder) calculus. These findings suggest acalculous cholecystitis. Ultrasound case study is courtesy of Dr. Vikas Shukla, MD, India.
Reference:http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/365553-overview (free article and images).
Acute cholecystitis- case-2
This patient had severe tenderness in the right hypochondrium. Ultrasound images show normal liver with edematous and grossly thickened gall bladder wall (10 mm.). There is also a small fluid collection around the gall bladder. These ultrasound findings are diagnostic of acute cholecystitis (acalculous). Ultrasound images of this case were taken with a Philips HD 15 ultrasound system. Color Doppler image however shows no significant vascularity around the gallbladder.
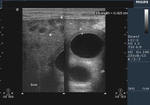
Calculous cholecystitis
This female patient underwent sonography of the gall bladder which showed a large calculus (6 cms.) within the lumen. The gall bladder (GB) walls show considerable thickening with layers of hyperechoic and hypoechoic regions. These ultrasound images are suggestive of calculous cholecystitis. In this case, the GB calculus obstructs the flow of bile with resulting edema and inflammation of the GB wall. Images are courtesy of Shlomo Gobi, Israel.
Reference: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/171886-overview
Chronic cholecystitis
This male patient presented with chronic right hypochondrial pain which did not resolve despite medication. Sonography of the gall bladder showed a thickened and shrunken gall bladder with absence of wall edema. Despite being nil orally, the gall bladder failed to distend and remained markedly echogenic. The gall bladder lumen was not adequately imaged but failed to reveal any calculi. These ultrasound findings are consistent with chronic cholecystitis. Repeated ultrasound imaging of the gall bladder in such cases show no alteration. Repeated episodes of inflammation of the gall bladder or long standing infection is believed to result in fibrosis of the gall bladder walls causing chronic cholecystitis. Unlike acute inflammation of the gall bladder, in chronic cholecystitis, there is no evidence of GB wall edema (as in the multi layered wall and distended lumen of acute cholecystitis). Ultrasound images of chronic cholecystitis are courtesy of Dr. Vikas Shukla, MD, India.
References:
http://www.efsumb.org/ecb/ecb-ch05-biliary.pdf(free article and images)
http://www.radiologyassistant.nl/en/43a0746accc5d
http://radiographics.rsna.org/content/24/4/1117.full.pdf+html (free article/ images on GB
imaging)http://www.ajronline.org/content/132/4/581.full.pdf
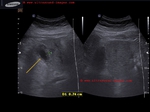
3D ultrasound imaging of gallbladder polyps
This patient was found to have multiple small gallbladder polyps on 2D ultrasound imaging. It is often a straightforward diagnosis. However, the 3D ultrasound images show the internal surface rendering in fine detail, demonstrating the gall bladder polyps despite their small size. This is often useful to the surgeon as well as for the patient to appreciate the nature of the gallbladder polyps.
These 3-D ultrasound images of multiple gallbladder polyps is courtesy of Dr. Sanjiv Bhalla, MD, India.
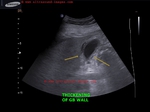
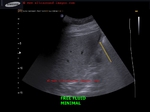
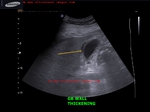
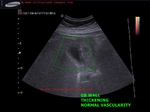
gallbladder-wall-thickening-dengue
This 50 yr female patient had abdominal pain and was clinically diagnosed to be suffering from dengue.
Ultrasound scan shows- minimal free fluid near right lobe of liver
- thickening of gallbladder wall (more than 7mm. in this case)
- striated pattern of gallbladder wall
- lack of abnormal or increased vascular flow in GB on Power Doppler study.
Increased thickness of gallbladder wall is a common ocurrence in dengue as multiple studies have shown.
There are reported to be 5 different varieties of GB wall thickening in dengue as imaged on sonography.
a) uniformly echogenic layer
b) striated pattern (as in this case)
c) tram track pattern
d) honeycomb pattern
e) focal thickening
(We used a Samsung Acuvix ultrasound system to capture these images).
References: sonographic changes and wall thickening of Gallbladder in dengue